Redshift Optimization
Last modified: December 09, 2019
What is Redshift?
Redshift is a fully managed, columnar store data warehouse in the cloud hosted by Amazon Web Services(AWS). Redshift can handle petabytes of data and is accessible 24/7 for their customers.
Redshift has many advantages for companies looking to consolidate their data all in one place. It is fully managed, very fast, highly scalable and is a part of the high used AWS platform.
Fully Managed
Amazon Redshift is fully managed, meaning that Redshift does all of the backend work for their customers. This includes setting up, managing, and scaling up the database. This means that Redshift will monitor and back up your data clusters, download and install Redshift updates, and other minor upkeep tasks.
This means data analytics experts don’t have to spend time monitoring databases and continuously looking for ways to optimize their query performance. However, data analysts do have the option of fully controlling Redshift, this just means they have to spend the time to learn all of Redshift’s functionality and how to use it optimally for themselves.
Very Fast
Redshift databases are very fast. Redshift databases are designed around the idea of grouping processing nodes known as clusters. Clusters are broken into two parts: a single leader node and a group of computer nodes.
The Leader Node is responsible for:
- Developing query plans
- Assigning tasks to processing nodes to optimize performance.
- Receiving and compiling all of the data returned by the processing nodes.
Processing nodes are responsible for:
- Performing the queries that are assigned to it by leader node.
There are two types of processing nodes:
- Dense Store(DS)- Dense stores nodes are stored on large Hard Disk Drives(HDDs), which are cheaper and have a higher capacity, but are slower than DC nodes.
- Dense Compute(DC)- Dense compute nodes are stored on Solid State Drives(SSDs) which give them the advantage of being a lot faster, depending on the task and drive types SSDs can be anywhere from 4 to 100 times faster than HDDs, but they are also more expensive and smaller capacity than DS nodes.
There are several tiers of processing nodes that have varying levels of storage and memory capacities. As databases grow or become more heavily queried, Redshift will upgrade the node tiers to maintain performance levels. More information on node type and pricing can be found here.
Data is stored across processing nodes in smaller subsections of a processing node which are known as slices. Slices are assigned a portion of the processing node’s memory, the quick access store used to hold data while it is in use, and storage, the long term storage location for the database, to manage queries on.
Data is assigned to the processing node’s slices by the leader node and is stored evenly across all of the processing nodes in the database.
Following this structure, Redshift has had to optimize their queries to be run across multiple nodes concurrently. Query plans generated in Redshift are designed to split up the workload between the processing nodes to fully leverage hardware used to store database, greatly reducing processing time when compared to single processed workloads.
Below is an image provided by AWS to explain their cluster interface:
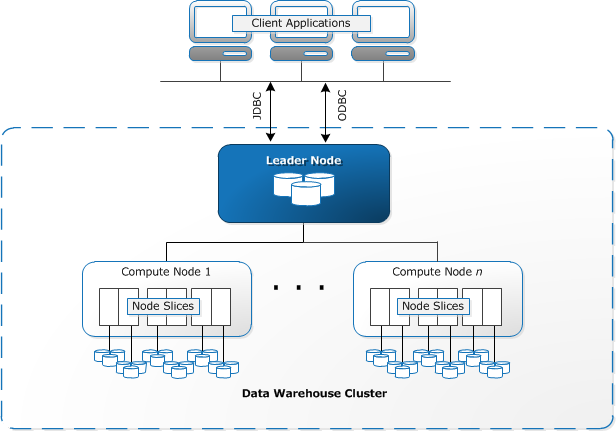 Source: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/redshift/latest/dg/c_high_level_system_architecture.html
Source: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/redshift/latest/dg/c_high_level_system_architecture.html
Redshift is one of the fastest databases for data analytics and ad hoc queries. Redshift is built to handle petabyte sized databases while maintaining relatively fast queries of these databases.
Data Compression
Redshift uses a column oriented database, which allows the data to be compressed in ways it could not otherwise be compressed. This allows queries to perform faster because:
- Data takes up less space in memory
- Compression reduces the cost on the CPU
- Can provide optimizations for certain queries that cannot be performed on decompressed data
Data compressions allows for increased performance of the database at the cost of more complex query plans. For the end user, this complication of query plans has no effect and is one of the reasons it is so heavily used.
Highly Scalable
Being stored with the cluster system explained above means that Redshift is highly scalable. As your database grows and expands past what your current configuration can handle, all that needs to be done to reduce query times and add storage is add another processing node to your system. This makes scaling your database over time very easy.
While query execution time is decreased when another node is added, it is not decreased to a set execution time. As processing nodes are added, query plans take longer to form and transferring from many nodes takes greater time.
If your database become more heavily queried over time you may also have to upgrade the node types you are using to store your database. Redshift will do this automatically to maintain a high level of performance.
Query Optimization
As databases grow, the settings used to create the database initially may no longer be the most efficient settings to run your database. To address this, Amazon created the “Schema Conversion Tool” that allows you to easily migrate an existing database into a new database with new, more optimized settings. A guide on migrating your slow database can be found here.
AWS Platform
AWS is an ever expanding cloud platform provided by Amazon. AWS is widely used in the business space to host websites, run virtual servers, and much more. Redshift is a part of Amazon’s ecosystem which means it can be easily linked with other Amazon services like: S3, DynamoDB, and Amazon EMR using Multiple Parallel Processing(MPP). MPP is the process of using multiple process nodes to speed up the transfer of data. When all of your services are on AWS you can optimize more than just your data queries by improving transfer times to other databases or buckets on your AWS account.
Another benefit of being on the AWS platform is the security. AWS allows you to grant very specific security clearances to their AWS instances and the same goes for Redshift. You can create a variety of “Security Groups” and “IAM”(Identity and Access Management) settings to lock down your data and keep it safe from outside groups. This optimizes time savings by freeing users from having to maintain third party security settings.
Summary
- Redshift is fully managed by AWS and does not require maintenance by the customer
- Redshift is very fast thanks to their cluster system of dividing work between processing nodes.
- These nodes are divided further into slices where the data is actually stored and queried
- Redshift is highly scalable because of the cluster system, expanding is as easy as adding another node and redistributing data.
- Redshift benefits from being a member of the AWS family and can be used seamlessly with several other AWS products.
- AWS also provides a layer of security for Redshift
References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/redshift/latest/mgmt/welcome.html http://db.csail.mit.edu/madden/html/theses/ferreira.pdf https://hevodata.com/blog/amazon-redshift-pros-and-cons/
Written by:
Blake Barnhill
Reviewed by:
Matthew Layne
,
Matt David
