Start Modeling Data
Last modified: August 24, 2020
Data Modeling sounds really scary, like a big chore and months of work.
But it is not so bad and you can get started in less than 10 minutes.
For this example we use BigQuery and dbt. BigQuery is one of Google’s cloud database offerings. dbt which stands for Data Build Tool is a data modeling tool created by Fishtown Analytics.

https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/
BigQuery comes with a set of public data sets that are great for practicing data modeling on. I will be using the Stack Overflow data set they have.
You can start using Google Cloud’s various services for free but you will need to upgrade the billing so that you can connect dbt to Google Cloud. If you have not signed up for Google Cloud platform services before they will give you a $300 credit (which is more than enough to run this test thousands of times) so don’t worry about the costs in trying this out.
Installing dbt

To install you can visit their documentation page here:
https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/macos
Or you can follow along below, most of what is here is straight from their docs anyways.
I suggest using homebrew to install dbt, it makes it extremely easy. If you do not have homebrew open your terminal on your Mac and put in the following command.
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
After it installs put the following commands into terminal.
brew update
brew tap fishtown-analytics/dbt
brew install dbt
You will also need git:
brew install git
Create a folder on your computer (I named my dbt Projects). We are going to populate it with all the files and subfolders dbt needs to get started. We do this by navigating into that folder through the terminal.
Then we run the following inside of terminal.
dbt init [name of project]
I called mine BQSO, so my terminal command looked like this:
dbt init BQSO
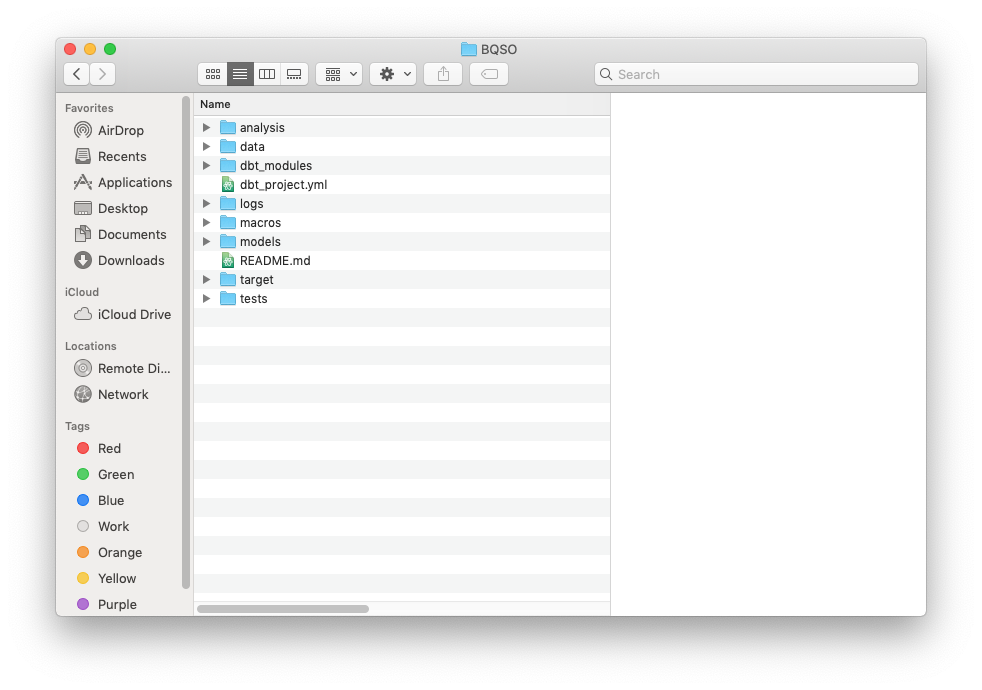
Navigate inside the folder to see all the folders and files dbt created for us
cd BQSO
Configuring BigQuery
To get dbt to work with BigQuery we need to give it permission. The way to do this is by setting up profile (think account) with login information. Basically you have to create a profile in dbt’s folder and then you will link that profile to this specific DBT project that you just created.
Go to dbt’s profiles (a sample profiles.yml file was created when we ran the dbt init command)
open /Users/[your username]/.dbt
This will pop open a file called profiles.yml which is the most challenging part of this tutorial. Configuring the profiles yml file. As a starter you can copy paste the code below to replace what is in the file, replacing one field with your own information.
my-bigquery-db:
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
type: bigquery
method: service-account
project: happy-vegetable-211094
dataset: soCleaned
threads: 1
keyfile: /users/matt/BigQuerykeyfile.json
timeout_seconds: 300
Now I will mark where you will need to update with your own info with bold.
my-bigquery-db:- This is the name which will be used to link the profile (account details/login info) to the project.
- I think this name makes sense but feel free to change it to whatever name you would like.
type: bigquery- The type of database, no surprises here.
method: service-account- How you will connect. This is specific to the database chosen, for bigquery this is how you do it.
project: healthy-terrain-239904- update with your own info
- This is the project name, it will be a weirdly named thing inside of BigQuery on the left.
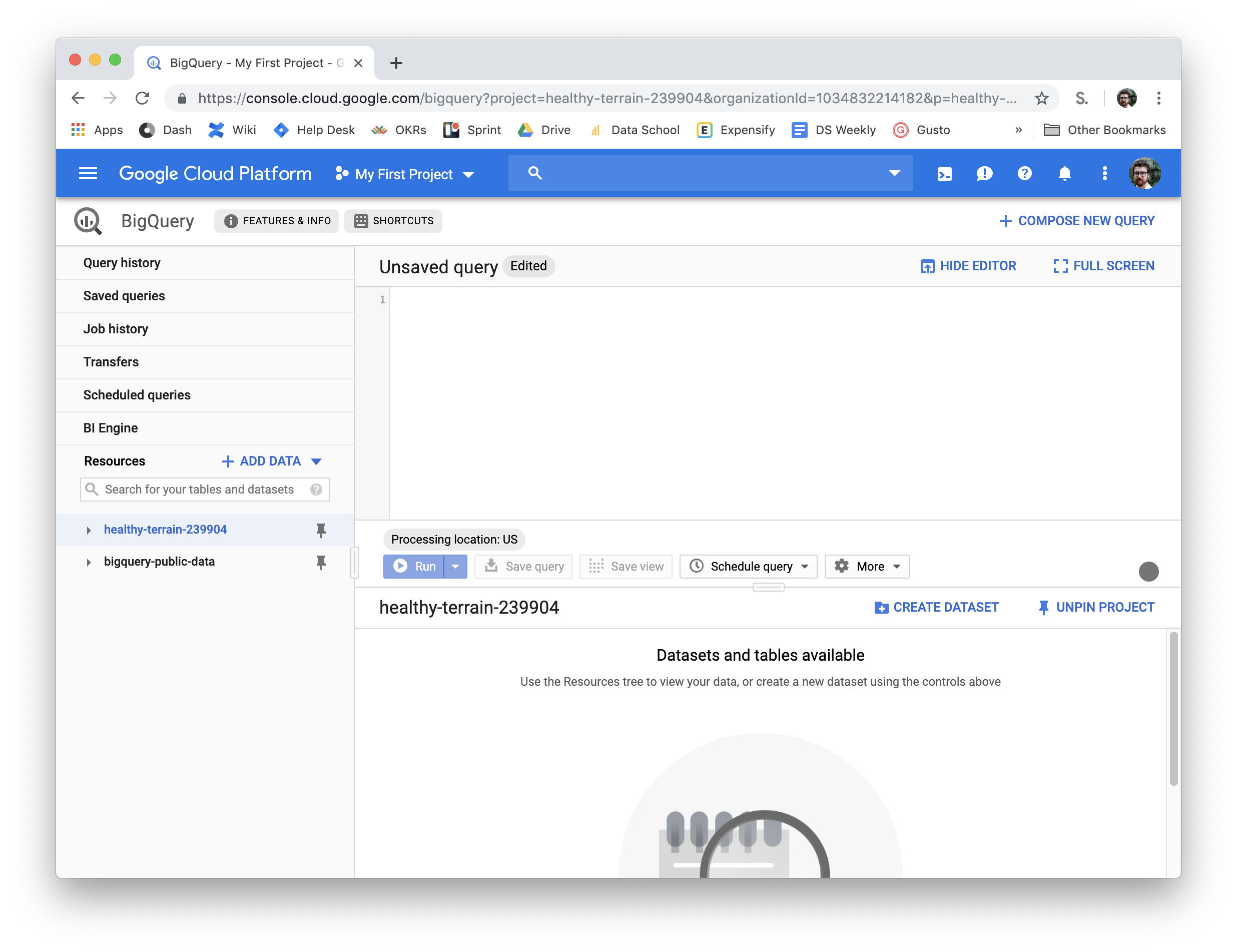
- Replace healthy-terrain-239904 with your project name.
- You may need to create a new project in BigQuery but there should be a default one which is fine to use for this example
dataset: soCleaned- update with your own info
- The name of Schema (Schema are called datasets in BigQuery) you will be putting the modeled data in
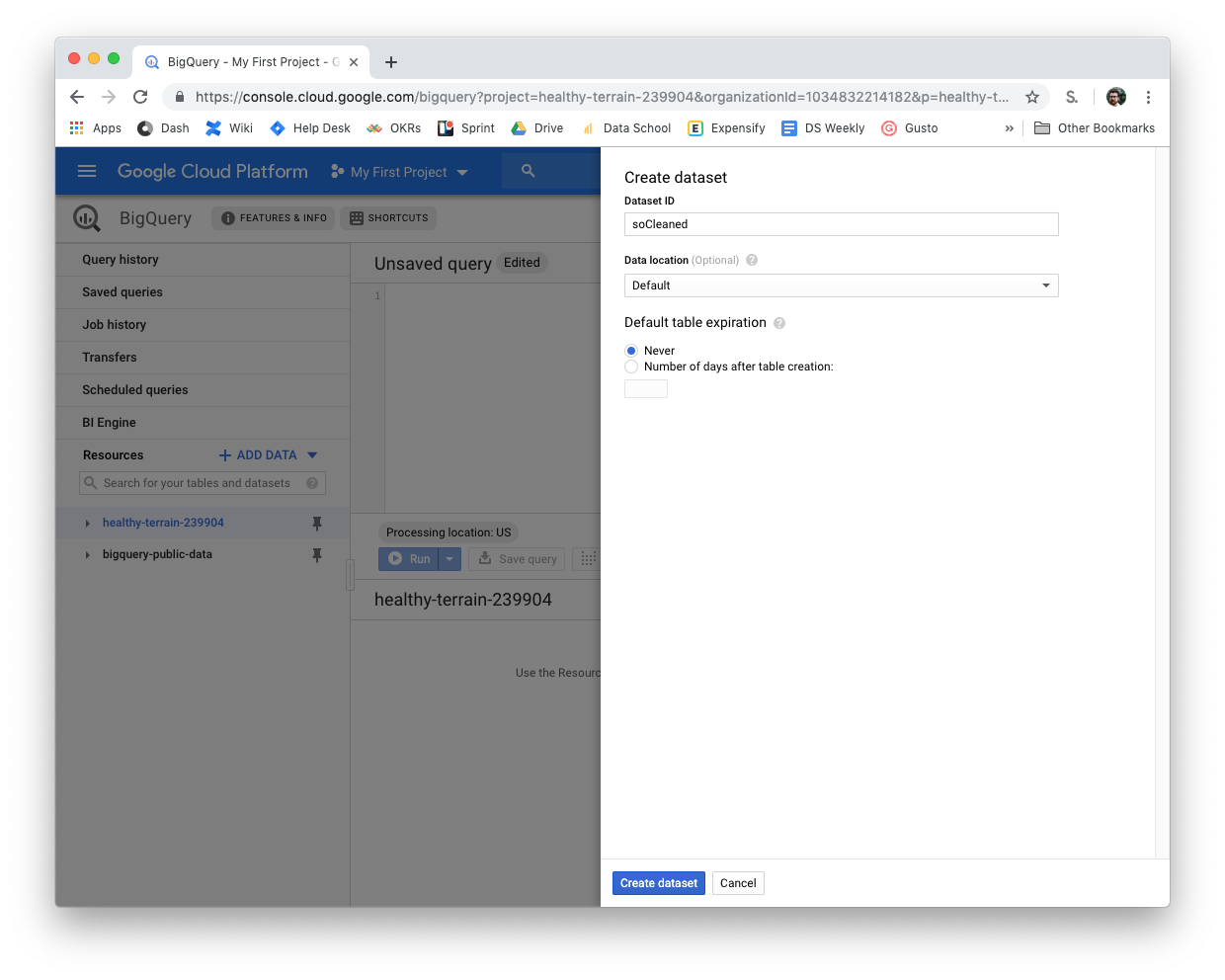
- Inside of BigQuery click on your project (healthy-terrain-239904)
- On the right you will see Create Data Set, click that
- The Dataset ID will be the name of the schema
- Replace soCleaned with your schema name that you put in the Dataset ID
keyfile: /users/matt/BigQuerykeyfile.json- update with your own info
- You do this by going to IAM & admin in BigQuery (hidden in the hamburger menu on the left)
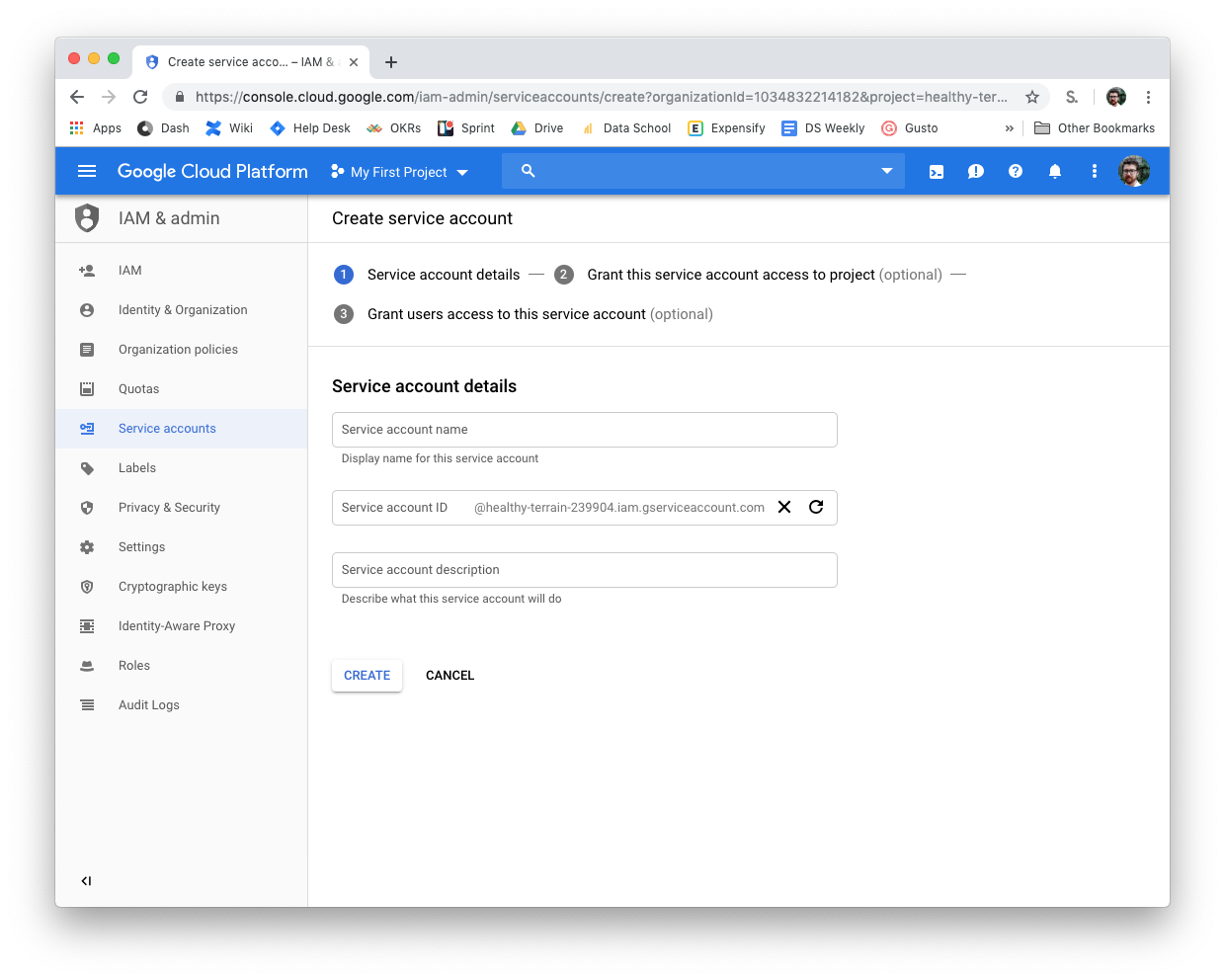
- Click Service Accounts
- Click Create Service Account
- Create a name for it (a name like dbt)
- Select Role - BigQuery Admin
- Create key - JSON
- This will download the key to your computer
- You will need to put the file path in the yml file so place it somewhere that makes sense to you
Once you update all of those fields in your dbt profile (profiles.yml) you now need to link that profile to the project we created.
Go to the project folder we had created earlier (BQSO in my case) and open the yml file inside of it.
dbt_project.yml
Now you only need to update one thing in this file, you need to se the profile to the name we just created:
profile: 'my-bigquery-db'
This is the link to the profile we just created, so if you changed that name to something else replace ‘my-bigquery-db’ with whatever you created. It does need the single quotes around the name of the profile.
Creating a New Table with Modeled Data
Go to the models folder in your project and create a new .sql file. In that .sql file you can write a SQL statement that’s output will be modeled data. Try adding this text to the .sql file and save it:
{{ config(materialized='table') }}
SELECT *
FROM 'bigquery-public-data.stackoverflow.posts_questions'
ORDER BY view_count DESC
LIMIT 1
Whatever you named the .sql file will be the name of the table in the schema (dataset) In my case I saved it as firstModel.sql
Running your Models
Go to terminal, make sure you are in the project folder of the dbt project and type
dbt run
Boom, refresh BigQuery and see the new table. You can query it with a simple.
SELECT *
FROM soCleaned.firstModel
Can you believe the most viewed post is about git? Classic.
You have now modeled data and queried modeled data. Not so scary right?
Why did we did we model this in the first place?
Well querying this modeled data took 0.2 seconds and processed 473bytes (granted this is just a single row with 20 columns)
When I do this query on the full Stack Overflow data set it took 20.3 seconds and processed 26.64 GB
How did this happen? We moved the larger query which operated on the full Stack Overflow data set to occur when we typed dbt run. dbt created a table with the results of that query which has one row of data. We then can query this new table which is much smaller through big query and get our result much faster. In fact we can query it as many times as we want without incurring the cost of the large query again.
Note: We will have to do dbt run again if we want to load the latest data into the modeled table. dbt run is often done on a schedule (typically at night) so that users know how up to date the data is they are dealing with.
There are many other things we can do with modeling and dbt such as cleaning up data, simplifying the schema, or find other ways to get more performance out of a query. Stay tuned for more!
Written by:
Matt David
Reviewed by:
Drew Banin
,
Dave Fowler
