Data Lake Maintenance
Last modified: October 30, 2019 • Reading Time: 5 minutes
Data Lakes are inherently not very well organized or maintained. They should be relatively low maintenance but there are two areas that will need some attention.
- Data Sources
- Performance
These maintenance activities can be expensive if you extracted and loaded your data with custom scripts. You would need in-depth knowledge of where data is coming from. You would need to know how to work with their API and data structures and potentially have to write a lot of new code when they make an update. Don’t Extract and Load manually, use tools like Fivetran, Blendo, or Stitch which will automatically handle these data source updates.
Data Sources
The main place where maintenance issues occur is when the data from the sources changes or the data is not making it from the source into the Data Lake.
Adding new data sources
Ideally, this is as simple as clicking a few buttons inside of an ELT product. Products such as Fivetran, Stitch, and Blendo have large numbers of connectors for different data sources:
.png)
https://fivetran.com/directory
https://www.stitchdata.com/integrations/sources/
https://www.blendo.co/integrations/
Data source updates
Sources change all the time, and ETL tools can handle these for you. This is what they focus on, so they will work to update API calls to make sure the data you’re getting is accurate.
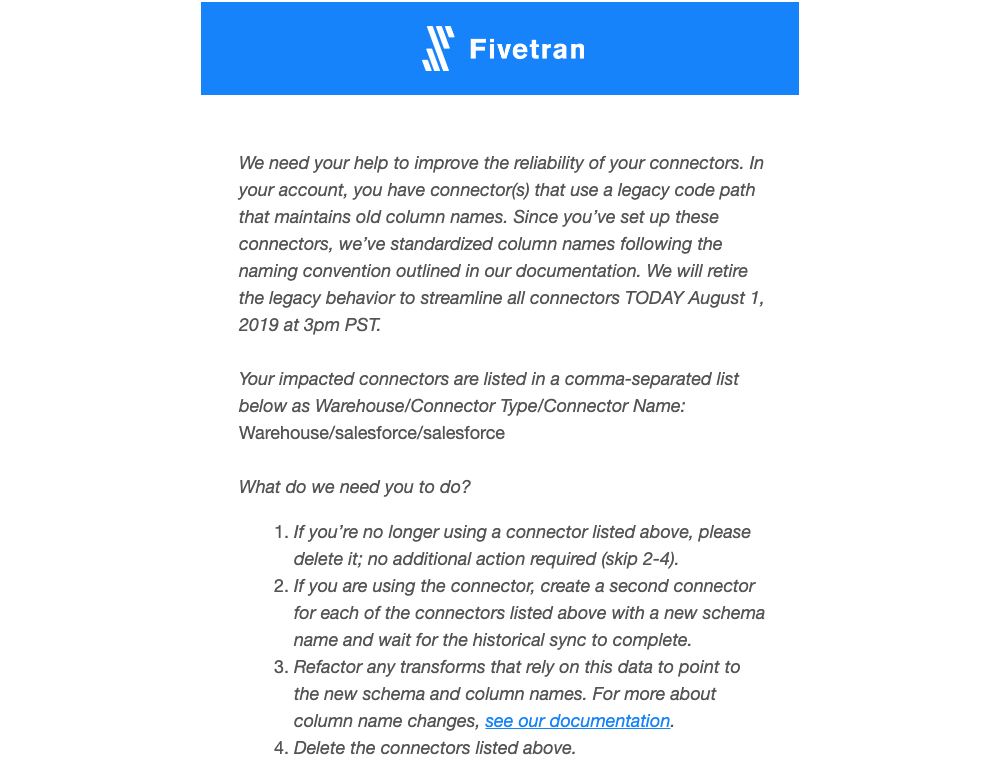
Fixing broken connections
Occasionally, you will need to manually reconfigure things. If a data source adds a new field or removes a certain table some of your queries might break. You will need to look into the changes and update your queries to work appropriately.
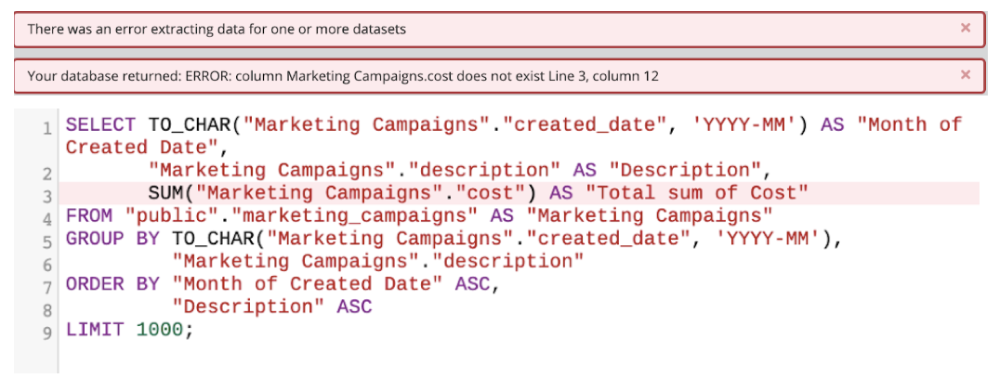
As shown in the case above, we need to consult the datasource and update the field name in the query. Therefore, to fix the query, we updated “cost” to “campaign_cost” as shown below.
.png)
Performance
At the Data Lake stage, you should focus your optimization at the dashboard or query level.
Optimize individual queries
There are simple concepts to keep in mind when optimizing queries. Only join what you have to, Select only the columns you will need to analyze, and so on. To dig in deep check out our Book on Optimizing SQL.
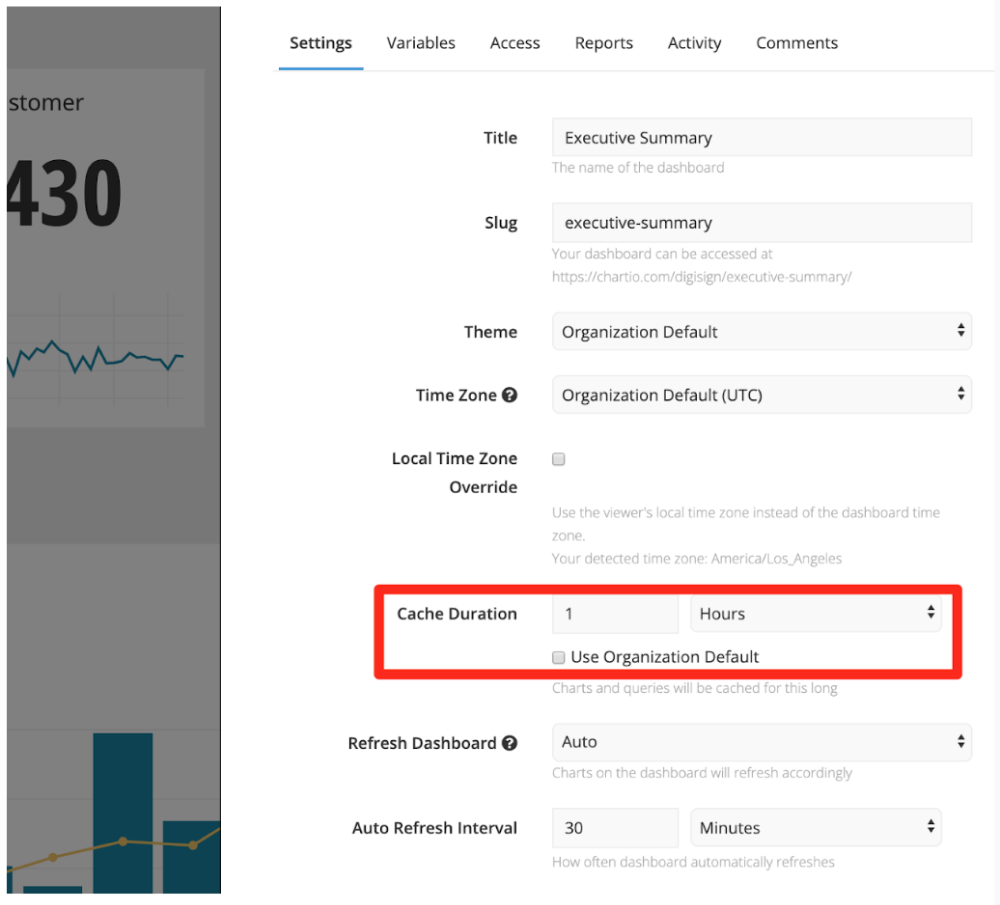
Caching
Many BI products allow you to cache data for improved query speeds and less strain on the database itself. While this reduces the real-time nature of your analytical query, you can query the data as much as you would like.
Create limits
Some platforms struggle with concurrency, where lots of people are querying the same source at once. Improve query speed in these scenarios by limiting how many queries people can perform on the database. While this can be a blow to people’s curiosity or analysis, it quickly solves this performance problem.
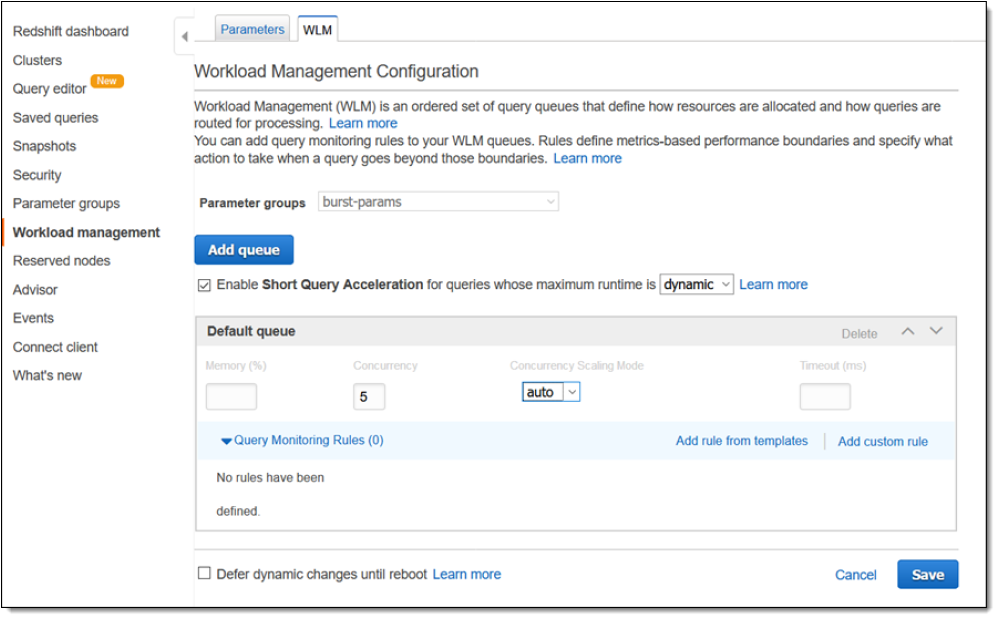
Queries can be limited in different ways:
- Limit number of people querying
- Limit queries per day
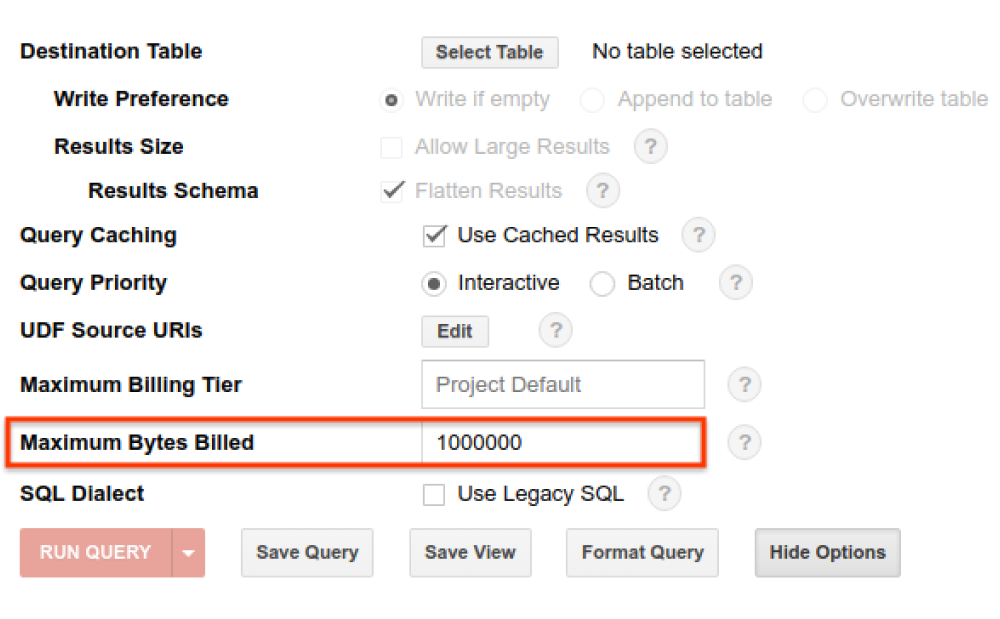
- Big Query - Set max bytes
Scheduling
Examine how your BI product queries the database. Does it do it automatically on a schedule or is it manual. Tools such as Chartio have options to schedule queries to run at off-peak times to balance the load on the database and Smart Refresh options to prevent queries from running when dashboards aren’t actively being viewed.
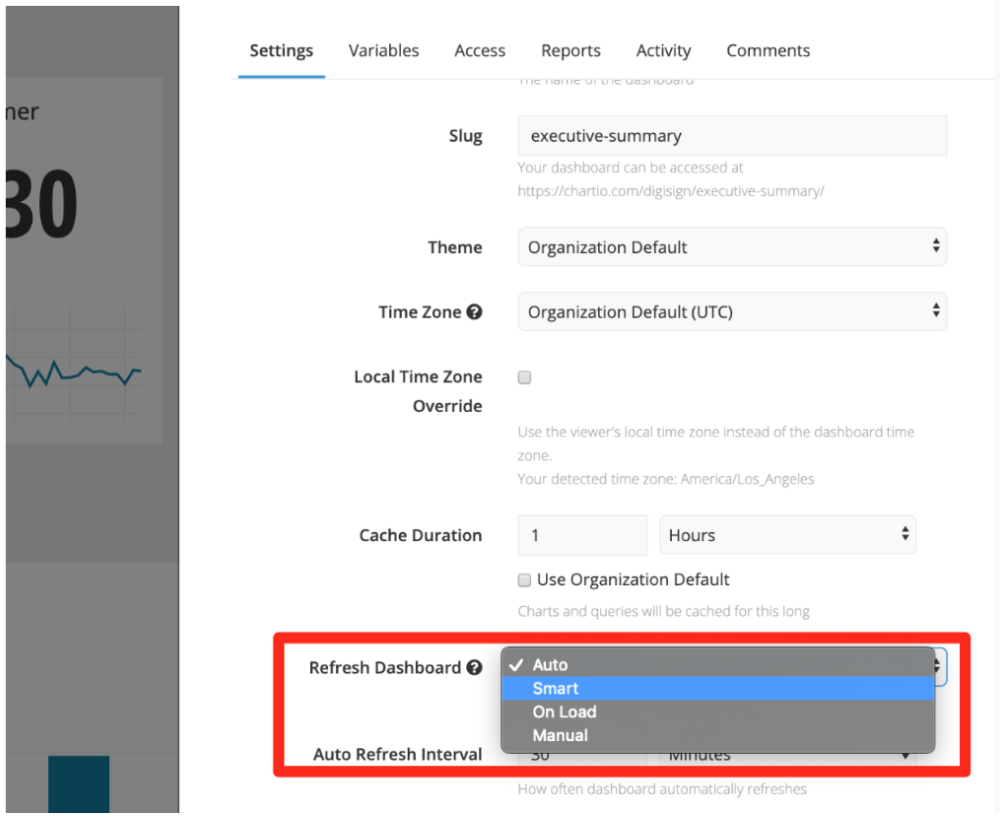
These sorts of tweaks become especially important as more users query the database.
Summary
To keep a Data Lake being useful you need to:
- Monitor data source connections and update pipelines when necessary. Use an ETL product to make this simple.
- Keep an eye on performance. More people will be querying the database in different ways. Optimize individual queries that are impacting the database, set up caching to improve speed, create limits to stop people from over-querying, and schedule how your BI tool refreshes queries.
Written by:
Tim Miller
Reviewed by:
Matt David
