Outputting Query Results to Files with \o
Last modified: September 13, 2019
\o [filename].txt
[Query or Queries to write to file];
\o
Outputting query results to a file instead of the terminal allows the data to be saved later analysis. The results can be shared easily and provide a snapshot of the data at the time of the query.
In order to output to a file, several methods can be employed. In this article the \o method of writing to files will be explored. One other method is using either \copy or COPY which are discussed in this article.
Video
The \o metacommand
\o is a metacommand. This means that it is delimited by a new line in the terminal rather than being part of the query. Simply write the metacommand and then press enter/return to run the command.
\o works like this:
\o [filename].txt- This will start writing the results of subsequent queries and certain metacommands to the specified file.
- [Query or Queries to write to file];
- Since these lines are after
\o [filename], these queries will be logged to the file.- Depending on version, the results of
\das well as\di,\dt, etc will be printed to the new file. (see example below) \!Commands will not be printed to the file.- If the output of a command is logged on the console, this means that it was not written to the file. If the result is not shown on the console, then the result was sent to the file
- Depending on version, the results of
- Since these lines are after
\o- Using
\oagain will close the file. This means that after running\othe file is done being written and can not be reopened using\o [filename].txt. Running\o [filename].txtagain with the same filename will overwrite the file. - Can also be terminated with
\q
- Using
Example use
Let’s look at an example of \o being used:
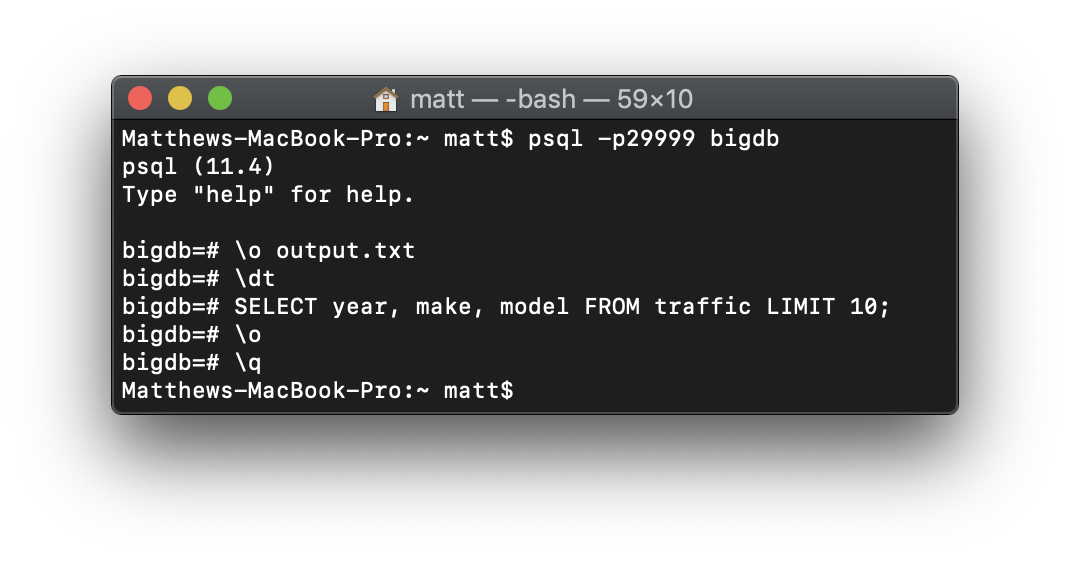
As you can see, the output of \dt and the SELECT query are not shown on the console. This indicates that they are being logged in the file. We can confirm this if we check the file. This can be done manually outside of psql or through psql using the \! meta command: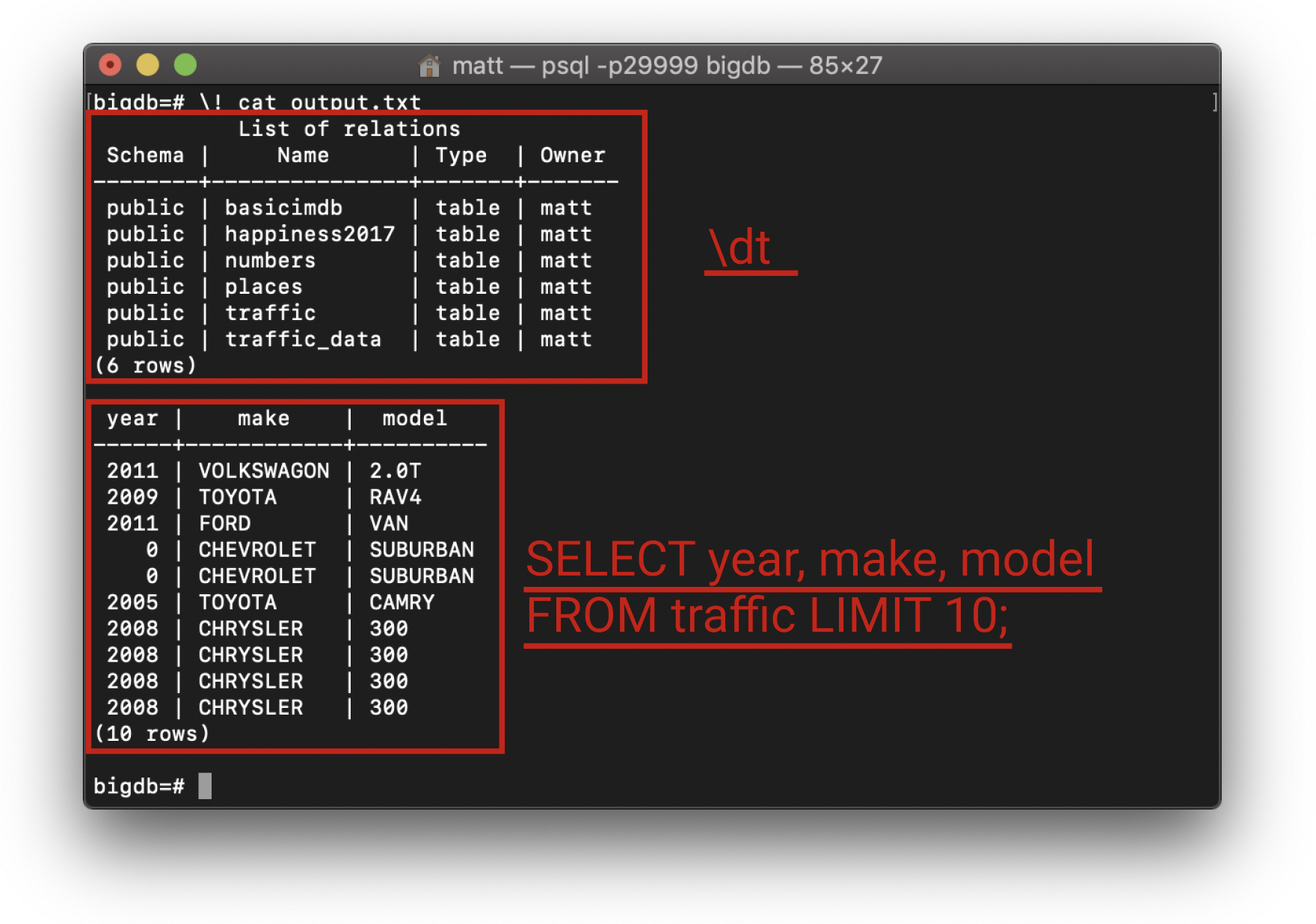
\! allows the user to use terminal commands and see the results without leaving the psql environment. As such, the file contents can be checked quickly using commands like cat which displays the contents of the text file to the screen.
Summary
\ocan be used to write query results to a file instead of the console:\o [filename].txt[Query or Queries to log to file];\o
- Can write the results of certain meta commands to the file.
- Can be checked using:
\! cat [filename].txt
Written by:
Matthew Layne
Reviewed by:
Matt David
